Ambien, known generically as zolpidem, is a widely prescribed medication used to treat insomnia. Its effectiveness in promoting sleep has made it a common choice for individuals struggling with sleep disturbances. However, understanding how long Ambien stays in your system is crucial, especially for those in recovery from substance use disorders. In this blog, we’ll delve into the duration of Ambien in the body, its potential side effects, and the importance of using sleep medications responsibly.
Together, let’s embrace the journey to recovery and the promise of a new beginning. Call us at (833) 503-0734 today or reach out online.
What Is Ambien?
Ambien is classified as a sedative-hypnotic medication, which means it is designed to induce sleep. It works by enhancing the effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter that inhibits nerve activity in the brain. By increasing GABA’s calming effects, Ambien helps users fall asleep faster and stay asleep longer. While Ambien can be effective for short-term insomnia treatment, it poses risks that need to be considered, especially for individuals with a history of substance use.
Understanding Ambien Addiction
Ambien is a sedative primarily prescribed for short-term management of sleep disorders. While it can be effective for many, its potential for misuse can lead to serious health risks, including:
- Physical Dependence: Regular use can lead to tolerance, meaning that over time, individuals may require higher doses to achieve the same sedative effects. This cycle can lead to increased usage and, eventually, physical dependence.
- Psychological Dependence: Many users may come to rely on Ambien as a crutch for sleep, resulting in anxiety about sleeping without the drug. This can create a vicious cycle of usage and dependence.
- Withdrawal Symptoms: If use is suddenly stopped, individuals may experience withdrawal symptoms, including insomnia, anxiety, irritability, and in severe cases, seizures.
How Long Does Ambien Stay in Your System?
The duration Ambien remains in your system can be influenced by several factors, including dosage, individual metabolism, and frequency of use. Here’s a breakdown of how long Ambien can be detected:
- Half-Life: The half-life of Ambien is approximately 2.5 to 3 hours. This means that after 2.5 to 3 hours, half of the drug is eliminated from the body. However, complete clearance may take longer.
- Detection Times: Ambien can be detected in various biological samples for different durations:
- Urine: Generally detectable for 1 to 2 days after last use.
- Blood: Typically detectable for about 6 to 20 hours.
- Saliva: Can be detected for 1 to 2 days.
- Hair: Potentially detectable for up to 90 days, though hair tests are less commonly performed for this purpose.
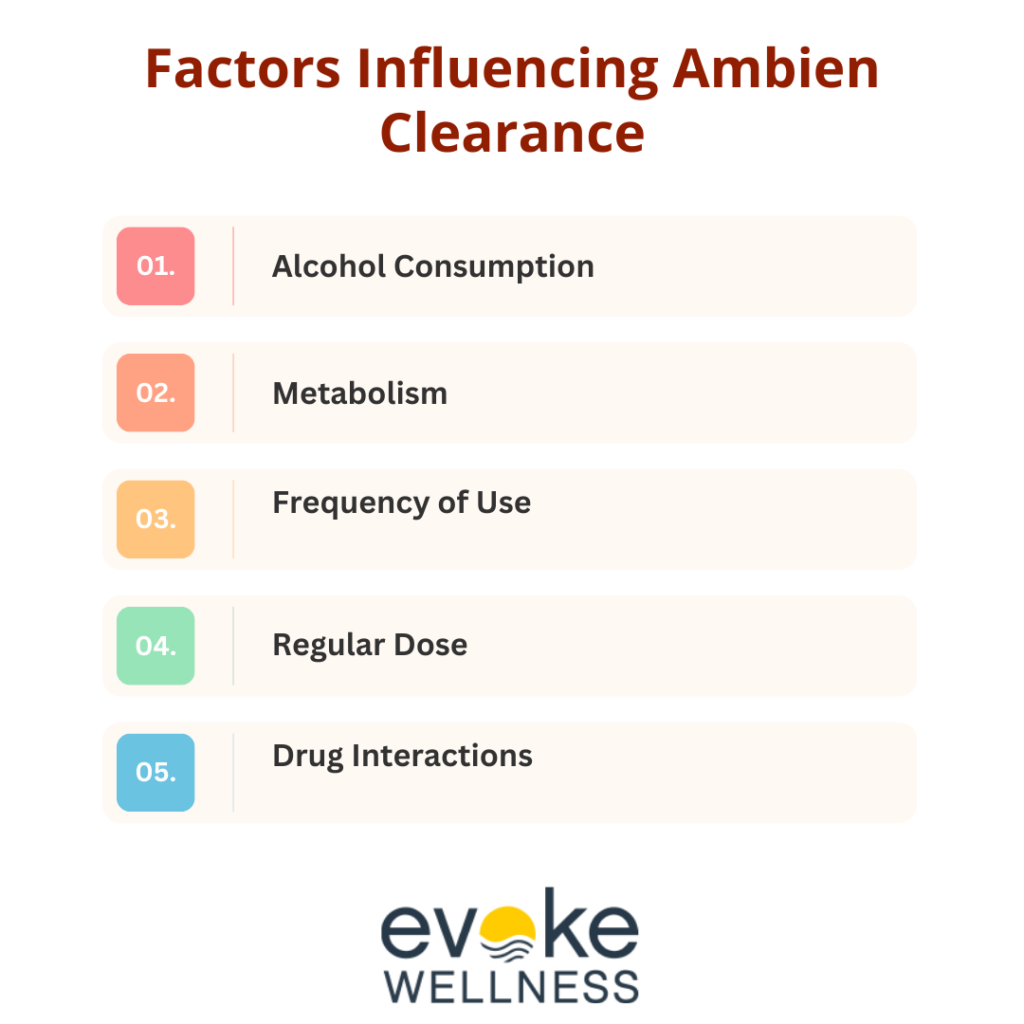
Factors Influencing Ambien Clearance
Several factors can influence how long Ambien stays in your system:
- Dosage: Higher doses may take longer to clear from the body compared to lower doses.
- Frequency of Use: Regular users may accumulate the drug in their system, prolonging its presence.
- Metabolism: Individual metabolic rates can vary significantly; those with faster metabolism may eliminate the drug more quickly.
- Age and Health: Older adults and individuals with liver or kidney impairments may metabolize Ambien more slowly, leading to longer detection times.
- Other Medications: Concurrent use of other medications can impact how quickly Ambien is processed and eliminated.
The Detectability Window of Ambien
The detectability window of Ambien, or zolpidem, can vary significantly based on several individual factors. Understanding these can help users manage their medication more responsibly, especially in the context of recovery. Here’s a closer look at the key factors that influence how long Ambien remains detectable in your system:
1. Age
Age plays a significant role in how quickly the body metabolizes medications. Older adults may process Ambien more slowly due to changes in liver and kidney function, leading to a longer detectability window. As we age, our body’s ability to eliminate substances decreases, which can affect the duration Ambien remains in the system.
2. Gender
Gender can also influence the metabolism of Ambien. Research shows that women often have a slower metabolic rate than men, leading to higher blood levels of the drug for a longer period. This difference is partly due to variations in body composition and hormonal factors, which can extend the time Ambien is detectable.
3. Weight
Body weight can affect drug distribution and elimination. Individuals with a higher body weight may have a larger volume of distribution for Ambien, potentially leading to lower peak concentrations in the bloodstream. Conversely, those with lower body weight may experience a more prolonged effect, as the drug can remain in their system longer.
4. Liver and Kidney Health
The health of your liver and kidneys is crucial in determining how efficiently your body can process and eliminate Ambien. Impaired liver or kidney function can slow down the metabolism and excretion of the drug, resulting in a longer detectability window. Individuals with liver or kidney issues should consult healthcare providers for personalized advice regarding Ambien use.
5. Metabolism
Metabolism varies greatly among individuals and is influenced by genetic factors, overall health, and lifestyle choices. People with a faster metabolic rate may clear Ambien from their system more quickly than those with a slower metabolism. This factor can significantly impact how long the drug is detectable in urine or blood tests.
6. Frequency of Ambien Use
Regular use of Ambien can lead to accumulation in the body, increasing the duration it remains detectable. Those who take Ambien intermittently may find that it clears from their system more quickly than individuals who use it consistently. Long-term users may need to be aware of the potential for tolerance and dependence, which can complicate recovery efforts.
7. Regular Dose
The amount of Ambien taken can significantly impact how long it stays in the system. Higher doses may lead to more extended detectability, as the body requires additional time to metabolize and eliminate the drug. Following prescribed dosages is crucial for minimizing risks and promoting safer use.
Potential Side Effects of Ambien
While Ambien can be effective for treating insomnia, it carries a risk of side effects, some of which may be serious. Potential side effects include:
- Drowsiness: The intended effect can lead to excessive drowsiness the following day if the medication is taken too close to waking up.
- Memory Loss: Users may experience short-term memory loss or “blackouts,” especially if they do not get a full night’s sleep after taking the medication.
- Rebound Insomnia: After discontinuation, many individuals may experience rebound insomnia, where sleep disturbances return and can sometimes worsen.
- Dependency and Tolerance: Long-term use of Ambien can lead to physical dependence, increasing the risk of misuse, particularly among individuals with a history of substance use disorders.
- Psychological Side Effects: Some users report unusual behavior, including sleepwalking, driving while not fully awake, or engaging in other activities without memory of them. This can pose significant safety risks.
- Other Side Effects: Other common side effects may include dizziness, headache, nausea, and gastrointestinal issues. Rarely, serious side effects can occur, including allergic reactions or more severe cognitive impairments.
The Importance of Using Sleep Medications Responsibly
For individuals in recovery from substance use disorders, managing insomnia safely is critical. Here are some guidelines to consider:
- Consult a Healthcare Professional: Before starting or stopping any medication, including Ambien, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider. They can assess your specific situation and recommend a suitable treatment plan tailored to your needs.
- Short-Term Use: Ambien is typically intended for short-term use, ideally no more than a few weeks. Prolonged use can lead to dependence and may interfere with recovery efforts.
- Consider Alternatives: Explore non-pharmacological approaches to managing insomnia effectively. Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I) focuses on changing thoughts and behaviors that contribute to sleep problems. This therapeutic approach can be integrated into Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy Programs at an Addiction Treatment Center.
- Supportive Therapies: Engaging in therapy, such as Dialectical Behavior Therapy and Family Therapy Programs, can help address underlying issues contributing to insomnia and provide essential support during recovery.
- Monitor for Side Effects: If prescribed Ambien, closely monitor your response to the medication. Report any adverse effects to your healthcare provider to adjust the treatment plan as necessary.
- Educate Yourself: Understanding the effects of sleep medications and their potential for misuse is crucial for making informed decisions about your health and recovery.
Managing Insomnia Without Medication
For individuals looking to manage insomnia without medications, consider these strategies:
- Sleep Hygiene: Establish a regular sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at the same time each day. Create a comfortable sleep environment, free from distractions.
- Limit Stimulants: Avoid caffeine, nicotine, and heavy meals close to bedtime to promote better sleep.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise can help improve sleep quality, but try to avoid vigorous workouts close to bedtime.
- Relaxation Techniques: Practices such as deep breathing, meditation, or gentle yoga can promote relaxation and improve sleep.
- Limit Screen Time: Reduce exposure to screens (phones, TVs, computers) at least an hour before bed, as the blue light emitted can interfere with sleep.
Embrace Recovery Today
While Ambien (zolpidem) can be an effective solution for insomnia and anxiety when used correctly, it poses a significant risk of dependency and addiction when misused. Understanding the signs of addiction and seeking professional support can lead to recovery and a healthier lifestyle. Overcoming Ambien addiction is a challenging but achievable goal. With the right support and resources at Evoke Wellness at San Marcos, individuals can reclaim their lives and learn to manage their sleep issues without relying on medications. Remember, seeking help is a sign of strength, and you don’t have to face this journey alone.
Conclusion
Managing insomnia safely is essential, particularly for individuals in recovery. While Ambien can provide temporary relief, it is crucial to understand its duration in the body, potential side effects, and the risks associated with long-term use. Responsible management of sleep medications, combined with supportive therapies, can enhance the recovery journey and promote overall well-being. If you or someone you know is struggling with insomnia or substance use, reach out to a qualified healthcare provider or an Addiction Treatment Center for support. Together, let’s embrace the journey to recovery and the promise of a new beginning. Call us at (833) 503-0734 today or reach out online.
FAQ on How Long Does Ambien Stay in Your System?
How long does Ambien stay in your system?
Ambien generally stays in your system for about 1 to 2 days, depending on factors like dosage, frequency of use, and individual metabolism. Its half-life is approximately 2.5 to 3 hours.
What are the potential side effects of Ambien?
Potential side effects include drowsiness, memory loss, dizziness, nausea, and the risk of dependency. Some users may experience unusual behaviors, such as sleepwalking or driving while not fully awake.
Is it safe to use Ambien for long-term insomnia?
Ambien is typically intended for short-term use. Long-term use can lead to dependence and tolerance, making it important to consult a healthcare provider for alternative treatments.
What should I do if I experience side effects from Ambien?
If you experience side effects, contact your healthcare provider immediately. They can assess your situation and adjust your treatment plan as necessary.
Are there alternatives to Ambien for managing insomnia?
Yes, non-pharmacological approaches such as Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I), good sleep hygiene practices, and relaxation techniques can be effective alternatives for managing insomnia safely.